From Ancient Rituals to Modern Vapes
What Is Nicotine?
Nicotine has woven its way through human history for an estimated 2000 years. Its story is deeply intertwined with the tobacco plant, scientifically known as "Nicotiana Tabacum." This plant, belonging to the nightshade family that also includes tomatoes and potatoes, has been utilized by diverse cultures. As both a medicine and a stimulant for almost as long as recorded history.
Whether you're someone who smokes cigarettes, explores vaping, or utilizes nicotine replacement therapies, understanding the inherent nature of this addictive substance is crucial. You might be surprised to uncover the long and intricate relationship humans have had with nicotine.
Where Did Nicotine Come From?
The consumption of the tobacco plant has been a significant part of human culture for millennia. With indigenous tribes initially using it in medicinal and ritual ceremonies. The tobacco plant itself occurs naturally in the Americas. While the exact route to European shores remains debated, it's widely believed that Christopher Columbus brought tobacco back to Portugal in the late 1400s. Following his initial voyages to the "New World."
Both the plant, Nicotiana tabacum, and the chemical compound nicotine are named after Jean Nicot. A French ambassador to Portugal. In 1550, he sent tobacco seeds to Paris for cultivation. A rudimentary concentrate of nicotine was known to scientists by 1571.
The culture of smoking rapidly spread through Western society. With pipe and cigar smoking becoming prevalent in the 1600s. The tobacco industry flourished by the 1700s, with more and more people taking up the habit. Beyond recreational use, tobacco was even employed as an insecticide by 1763.
In 1828, Dr. Wilhelm Heinrich Posselt and chemist Karl Ludwig Reinmann, two German scientists, first managed to extract nicotine from the tobacco plant in its purest form. Notably, they were also the first to identify nicotine as a poison. Despite this alarming discovery, the invention of the first machine for mass-producing paper cigarettes in 1880 led to an explosion in tobacco consumption.
It wasn't until later in the 19th century that lawmakers began to acknowledge the harmful effects of nicotine. With 26 US states banning tobacco sales to minors by 1890. However, the US Surgeon General only published a definitive study linking smoking with heart disease and lung cancer as recently as 1964. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) officially recognized nicotine's addictive properties as late as 1994.
In the modern era, nicotine is accessible to the public in a diverse range of forms. While smoking the tobacco leaf remains the most common method of nicotine consumption, it can also be delivered via Nicotine Replacement Therapies like patches and gum, and of course, through vaping products or e-cigarettes. Our understanding of the harm that nicotine and smoking can cause is greater now than at any point in history. However, the intensely addictive nature of nicotine itself is likely the primary reason smoking continues to be a leading global cause of preventable death.
Beyond human consumption, the only other known application of nicotine is as a pesticide. However, its use in this area has declined significantly since World War Two, and it has even been banned in recent years due to the potential harm it poses to mammals (including humans!) at high concentrations.
The Science of Nicotine – What is it?
Nicotine is the intensely addictive compound found naturally within the tobacco plant. It constitutes approximately 5% of a tobacco plant's total weight. Despite making up only a small amount of nicotine compared to the overall plant material we inhale when we smoke cigarettes, it is nicotine that keeps people continuing to smoke, even when they desire to quit.
Nicotine is an organic chemical compound belonging to a group of substances called alkaloids. Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing compounds known to exert marked physiological effects of nicotine on humans. In fact, nicotine has been classified as a stimulant, much like caffeine or cocaine. Stimulants excite bodily functions, particularly the brain and central nervous system. They are known to induce alertness, elevated mood, wakefulness, increased motor activity, and a decrease in appetite – all effects commonly associated with smoking.
The Present and Future Of Nicotine
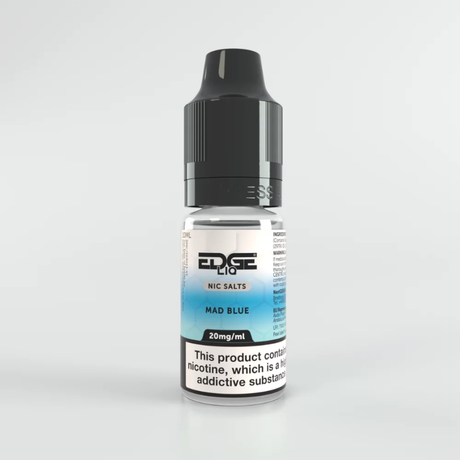
The latest advancements in nicotine delivery have emerged from the vaping industry itself, with the development of nicotine salt products like EDGE Bar Salts and EDGE LIQ. As discussed in our blog about nic salt e-liquids, standard nicotine is chemically combined with an acid molecule during manufacture. This process effectively neutralizes the naturally harsh alkaline taste of the nicotine. Enabling a vaping device to deliver a much higher dose of nicotine, such as the 20mg typical of nic salt e-liquids, without the associated harsh throat hit. Nic salts also absorbs nicotine faster than freebase nicotine (the nicotine used in standard e-liquid), crossing the blood-brain barrier with greater ease.
Looking ahead, the landscape of nicotine consumption is likely to continue evolving. While traditional smoking rates are declining in many parts of the world, alternative nicotine delivery methods are gaining traction.
Beyond vaping, innovations in areas like heated tobacco products, nicotine pouches, and even advancements in nicotine replacement therapies such as faster-acting gum and patches, are shaping how people consume nicotine. The focus is increasingly shifting towards harm reduction, with the development of products that aim to satisfy nicotine cravings without the harmful by-products of tobacco smoke. However, the long-term health implications of these newer methods are still being studied, and regulatory frameworks are continuously adapting to this evolving market. The future of nicotine will likely involve a greater diversification of products, driven by both consumer demand and public health considerations aimed at reducing the harms associated with traditional nicotine use.
EDGE Nic Salts
View allA Stepping Stone to Quitting Smoking and Reducing Nicotine
EDGE Nicotine Salts
For smokers looking to transition away from cigarettes, EDGE nicotine salts can be a valuable tool in their journey to quit smoking and ultimately reduce their nicotine consumption. The key lies in how nic salts effectively address the physical and psychological aspects of nicotine addiction.
One of the primary hurdles when attempting to stop using tobacco products is managing withdrawal symptoms. These can include intense cravings for nicotine, irritability, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, headaches, and even nausea. The rapid absorption of nic salts into the bloodstream, mimicking the delivery of nicotine from a cigarette, can help to alleviate these withdrawal symptoms more effectively than traditional freebase e-liquids. This can make the initial transition to vaping less jarring and more sustainable, reducing the urge to return to smoking.
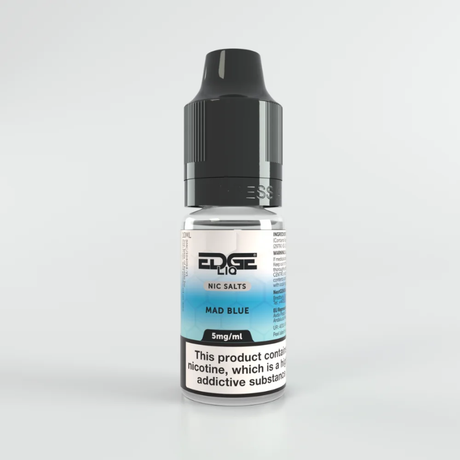
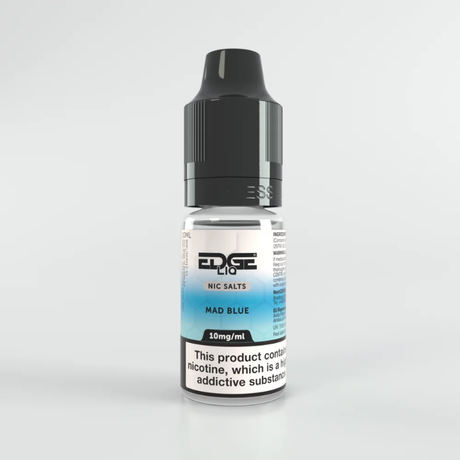
EDGE Liq nic salt e-liquids, with their range of nicotine strengths like 20mg, 10mg, and 5mg, offer a pathway to gradually reduce nicotine intake. A smoker accustomed to the high nicotine level in cigarettes might initially find the 20mg strength provides a similar level of satisfaction, curbing their cravings. As they become more comfortable with vaping and less reliant on the sensation of smoking, they can then step down to 10mg and eventually 5mg. This gradual reduction minimizes the intensity of withdrawal symptoms typically experienced when abruptly stopping nicotine.
Furthermore, the enhanced flavour delivery of nic salts can make the vaping experience more enjoyable. By focusing on satisfying flavours, individuals may find themselves less fixated on the nicotine itself. The availability of various flavour options in the EDGE Liq range can also help break the association with the taste of cigarettes.
It's important to remember that while vaping with nicotine salts is a less harmful alternative to continuing to smoke, the goal for many is to eventually eliminate nicotine consumption altogether. EDGE Liq nic salts provide a flexible starting point and a means to taper down nicotine levels, making the journey to becoming smoke-free and potentially nicotine-free more achievable.
To learn more about the impact excessive nicotine consumption can have on your body, explore the EDGE Best Practice Series: Understanding Nicotine Addiction.
Our Sources:




































